Epoxy resins have revolutionized numerous industries, providing exceptional mechanical properties, outstanding adhesion, and remarkable resistance to various environmental factors. Versatile materials, they are widely used in aerospace, electronics, and medical applications as well as in construction, automotive, and marine applications. The true potential of epoxy resins, however, can only be unlocked through a crucial process known as epoxy curing.
Epoxy resins offer manufacturers numerous benefits. In addition to having unique resistance and mechanical properties, the resins are also thermal, chemical, and water resistant, and durable. Some epoxy resins are curable at room temperature. But others need additional processing. Curing epoxy resins, however, is time-consuming and costly. Savvy manufacturers use epoxy-curing ovens to heat the resins, which cuts curing time by days, increases efficiency, and boosts productivity.
Understanding Epoxy Curing
Epoxy curing is a chemical reaction that transforms liquid epoxy resins into solid, cross-linked polymers. Adding curing agents or hardeners to the epoxy resin triggers the polymerization reaction. The curing agents act as catalysts, initiating the cross-linking of the resin molecules. That results in a three-dimensional network that provides the desired properties. Epoxy resins, however, don’t fully cure at room temperature. Adding heat with help from an epoxy curing oven accelerates the cure rate and boosts the material’s performance profile.
Adding heat to the curing process isn’t fully understood or appreciated by many manufacturers. But it’s critical to curing resins and their use. Adding heat to the post-curing process, for example, helps manufacturers achieve biocompatibility in medical device applications. Adding heat to the post-curing process also helps aerospace manufacturers optimize the epoxy’s properties and meet that industry’s many rigorous testing and qualification procedures.
Long Curing Times Decrease Efficiency
No matter the industry or the application, long cure times can impact a company’s efficiency and productivity, which also cuts into profitability. But using epoxy-curing ovens shortens curing times. Epoxy resin processing requirements include:
- Typical epoxy cure temperatures range from 100 °C to 275 °C, depending on material and application.
- Can range from 280 to 400 °C, depending on application.
- Generally, a nitrogen atmosphere is required with oxygen content below 100 PPM.
- Class 100 conditions or better.
- Good temperature uniformity
- Higher exhaust rates to remove fumes.
- Fast cycle times to improve throughput.
Put simply, adding heat to the epoxy post-curing process unleashes the full potential of epoxy resins, making them the go-to material in many situations. Key factors that can affect the curing process, however, include differences in temperature control set temperature versus the oven’s actual temperature, heating and cooling ramp rates, and variability of temperature within the oven (temperature uniformity).
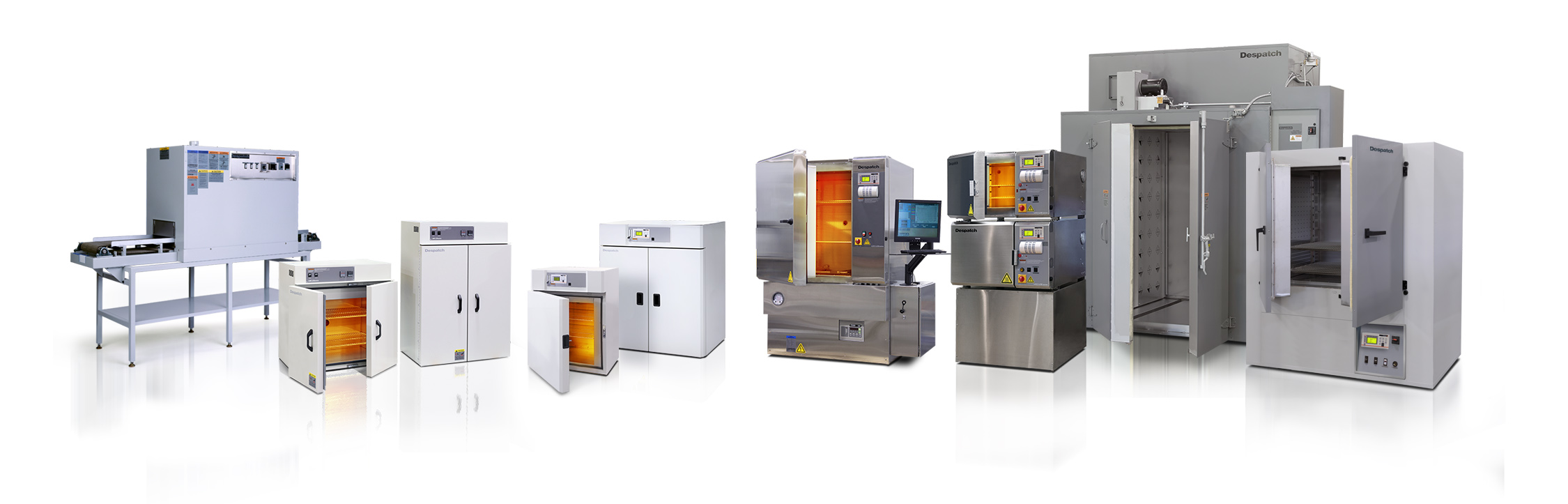
Despatch Ovens: Ideal for Curing Epoxy Resins
Despatch epoxy curing ovens, like its LCC Stackable Clean Process bench top oven, are ideal for curing epoxy resins. Rugged and reliable, they feature higher volumes of airflow with unique distribution for exceptional temperature uniformity. The oven’s features are well-suited to curing epoxy resins. Plus, the ovens can maintain Class 100/ISO Class 5 conditions at up to 5°C heating and cooling rates at stable conditions.
The use of the Despatch LCC1-51 Cleanroom Oven at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, described below, is instructive:
When the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center needed an oven to cure epoxy resins, it turned to Despatch’s LCC1-51 Clean Process oven. The main adhesives NASA uses in its application are 3M Scotch-Weld 2216 Gray, EPO-TEK T7110, and EPO-TEK H74. These are two-component, thermally conductive resins. To create high-strength bonds between the resin and substrate, NASA removes all surface contaminants, like paint, oxide films, oils, and dust, then cleans them using Isopropyl alcohol or ethanol. This operation prepares the item for bonding and drying.
Then, NASA applies a resin to the components and cures them in the LCC oven at 200°C, which creates high-strength bonds.

A Class A Oven, the LCC1-51 was a good choice for this application because it’s specifically designed for curing resins. The oven included features like an explosion relief panel, airflow switches, and a purge timer. Since solvents are involved in the application, the oven also had to be silicon-free. Silicone can create problems in these applications where even small amounts can stop adhesion later. To eliminate this problem, Despatch replaced the oven’s silicone door seal with a Viton seal and used non-silicone-based sealants in the oven.
Ideal when Failure is Not an Option
As the NASA application shows, Despatch’s Clean Room ovens are ideal for challenging applications where failure is not an option. These ovens are well suited to applications where curing epoxy resins quickly and efficiently is required. The ovens’ advanced technology and ability to provide exceptional temperature uniformity performance are critical to delivering uniform and repeatable thermal processing. These ovens not only help complete the curing process but also boosts efficiency, protects workers, and speeds up the curing rate. That, in turn, increases both productivity and profitability.
Despatch offers a wide selection of Curing ovens offering a range of chamber sizes and temperature capabilities. Please get in touch with us if you need more information about any of our ovens, from oven design and sales to installation and maintenance services.
Image by Michael Schwarzenberger from Pixabay