Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have made a big breakthrough in energy storage. They have improved a special type of concrete, called electron-conducting carbon concrete (ec³), so it can now store ten times more energy than before. This could turn ordinary walls, sidewalks, and bridges into batteries that store electricity.
What Is a Concrete Battery?
This concrete is not like the cement you see in regular buildings. Scientists mix cement, water, and tiny particles of carbon black to create a material that can conduct electricity. When they add a liquid called an electrolyte, this concrete can store and release electrical energy. In other words, it acts like a supercapacitor, which is a type of battery that can charge and discharge quickly.
Ten Times More Power
Before this improvement, storing enough energy for an average home required about 45 cubic meters of this concrete, about the size of a full basement. With the new version, only 5 cubic meters are needed, roughly the size of a single wall. One cubic meter can now store over 2 kilowatt-hours of energy, enough to run a refrigerator for a whole day.
Double Function: Strength and Energy
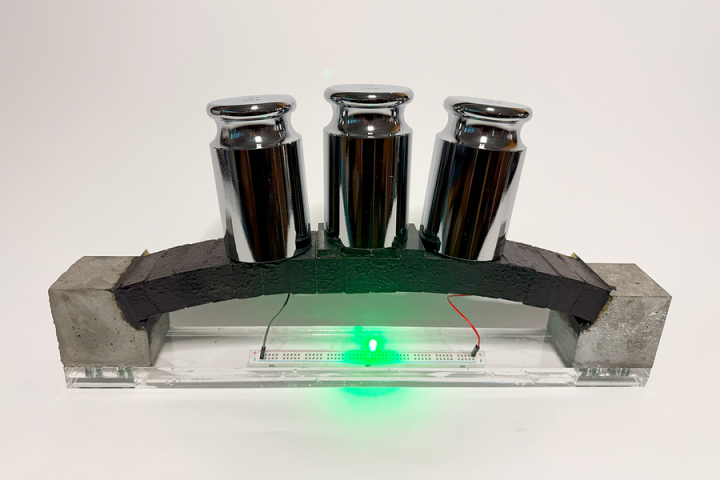
The best part is that this concrete is still strong and can hold up buildings while storing electricity. Scientists have even shown that a structure made of this concrete can light an LED, with the light changing depending on the weight applied. This could help monitor the health of buildings while also powering them.
Why It Matters
This breakthrough brings us closer to “smart concrete” that not only supports buildings but also stores energy. It could help store solar or wind power for use when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing. This technology may change the way we think about energy and the buildings we live in.
Image & article source: MIT