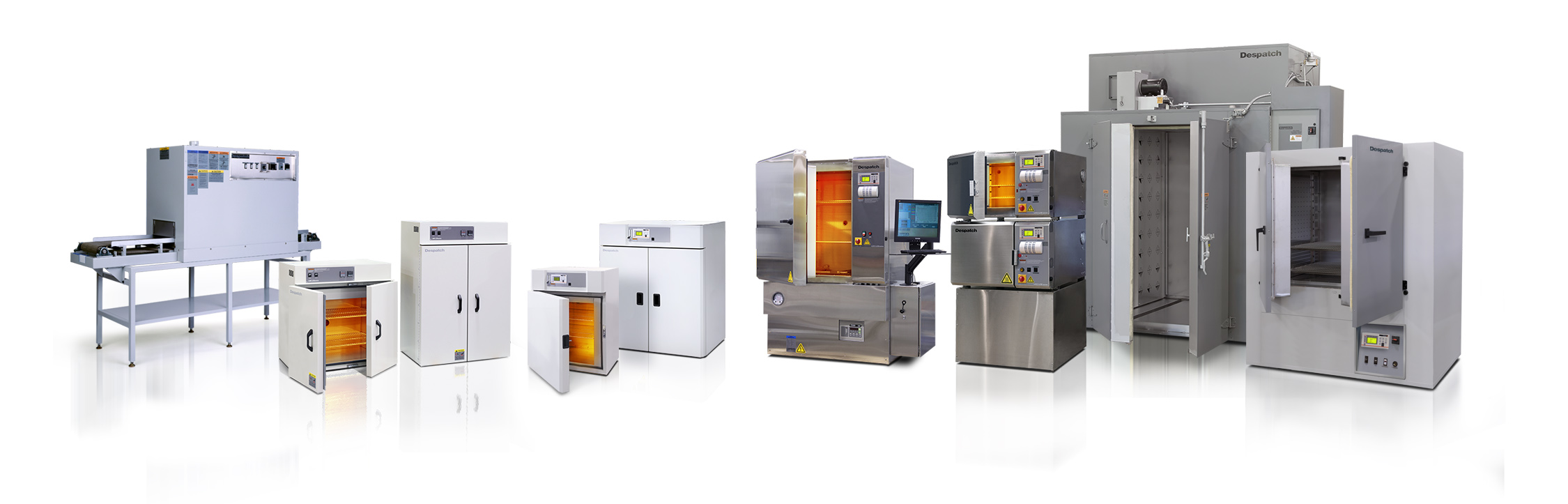
The pharmaceutical industry carries enormous responsibility in developing and manufacturing drugs. This activity involves numerous steps to ensure drug quality, efficacy, and safety. But creating safe, effective, high-quality drugs is challenging. Many companies are beating this challenge with the help of laboratory ovens.
Lab ovens, in fact, are among the critical tools pharmaceutical companies use when it comes to producing today’s medications. Versatile and adaptable, these unheralded tools contribute significantly to various stages of pharmaceutical research—from drying and sterilization to stability testing and process development.
Lab Ovens Offer Key Production Benefits
Pharmaceutical lab ovens offer diverse general benefits while helping companies create new medications and refine existing ones. These benefits include:
- Enhanced consistency
- Improved efficiency and throughput
- Enhanced safety and reliability
- Streamlined workflow and cost savings
- Increased accuracy and reliability
- Minimized waste and lower labor costs
It’s no surprise, then, that more and more pharmaceutical companies are turning to lab ovens to spearhead drug production.
The global market for pharmaceutical ovens is projected to reach a value of USD 2.4 billion by 2031 while registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.7% from 2022 to 2031, says Business Research Insights
Lab Ovens Boosts Production and Quality
Lab ovens boost production with help from capabilities like precise temperature and humidity control, real-time monitoring and data logging, oven automation and programming, and faster processing times—all while cutting downtime, lowering energy consumption, and providing dependable performance.
Other production advantages include accurate assessment of product degradation, elimination of microorganisms and toxins that can contaminate drugs, and continuous monitoring of ovens to ensure the process adheres to established protocols and regulatory requirements.
Lab ovens also boost the stability and quality of pharmaceutical applications thanks to their ability to provide precise temperature and humidity control. This capability helps:
- Boost reproducibility for research/development
- Maintain material integrity and quality
- Prevent the degradation of drugs
- Optimize specific process
- Help meet regulatory regulations
- Improve efficiency and process optimization
- Prevent uncontrolled reactions
Pharmaceutical companies can also use lab ovens to facilitate accelerated stability studies (ASS), which help predict drug shelf-life and degradation behavior under stressed conditions in a much shorter timeframe than real-time stability testing.
Plus, they can use lab ovens to facilitate heat-induced degradation studies that boost drug formulation optimization by investigating how a drug substance and its formulation components respond to elevated temperatures.
Types and Uses of Lab Ovens in Drug Formulation
Lab ovens come in various sizes and temperature ranges, with critical features like ventilation options and programmability. Plus, many of today’s lab ovens are energy-efficient, with help from advanced insulation and airflow management systems, lowering operating costs and cutting environmental impact. Lab oven variety enables researchers to choose units that best fit their needs and applications.
Below are a few of the different types of lab ovens used in pharmaceutical production, each offering unique advantages for specific applications:
- Mechanical convection—Offer faster drying times compared to gravity convection ovens. Suitable for various applications, including drying powders and granules.
- Gravity convection—Provide a simpler design than mechanical convection ovens. Suitable for heat-sensitive materialsthat might be susceptible to damage from forced air circulation.
- Vacuum—Well-suited for drying heat-sensitive drugs, biological materials, and volatile solvents. Minimize the risk of oxidationand degradation of sensitive materials.
- High-temperature—Used for sterilization of equipmentand depyrogenation of materials.
- Force air convection—Provide faster drying timesthan gravity convection ovens. Offer more uniform temperature distribution compared to purely mechanical convection ovens.
In addition to these ovens, you have batch, continuous, infrared, and cleanroom units. Each type has its advantages in pharmaceutical applications.
Below are some real-world examples of how lab ovens facilitate drug research, formulation, and production:
- Precipitates: Following chemical reactions, precipitates are often dried in lab ovens to remove solvents and isolate the desired product.
- Drying: Lab ovens are essential for drying various materials in drug development, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), ensuring consistent moisture content and optimal formulation characteristics.
- Excipients: Drying excipients like fillers, binders, or disintegrates to remove moisture that could affect their properties or the stability of the final drug product.
- Stability testing: Lab ovens can help create controlled temperature environments, enabling researchers to evaluate potential degradation pathways
- Biological samples: Lab ovens are used for drying tissues, enzymes, or other biological materials for analysis or storage, which often involves precise temperature control.
- Data integration: Advancements in this area allow companies to program complex temperature profilesand integrate data with other equipment.
Critical Advancements in Lab Oven Design
Lab oven design is continuously evolving, paralleling similar advancements in pharmaceutical research. Modern lab ovens have expanded temperature ranges, tools to facilitate comprehensive data analysis and process optimization, and automation features that can cut the need for human intervention. Additional advancements include better connectivity and remote monitoring and integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and other emerging production processes.
Despatch, for example, offers a walk-in lab oven for drying 3D-printed pharmaceuticals. Additive Manufacturing has only recently made its way into the pharmaceutical space – leading to new therapies. 3D printing allows the formulation of customized dosages and delivery methods not possible with conventional pharmaceutical production. It also allows for greater customization and personalization and reduces drug development time.
Lab Ovens are Reshaping Pharmaceutical Production
Modern lab ovens equipped with advanced features and precise control systems are shaping the future of pharmaceutical research, development, and production. Pharmaceutical lab ovens eliminate many of the disadvantages of conventional tablet production while providing flexibility and ease of design. They also boost the production processes to new levels while helping companies provide safe, effective, high-quality medications.
Put another way, lab ovens are helping pharmaceutical companies shoulder the enormous responsibility of developing and manufacturing drugs. Choosing the correct type of lab oven depends, however, on several factors, such as the application, temperature requirements, desired drying speed, material sensitivity, and budget constraints. Experienced manufacturers, like Despatch, can assist pharmaceutical companies in customizing lab ovens to their specific needs.
Image by PublicDomainPictures from Pixabay